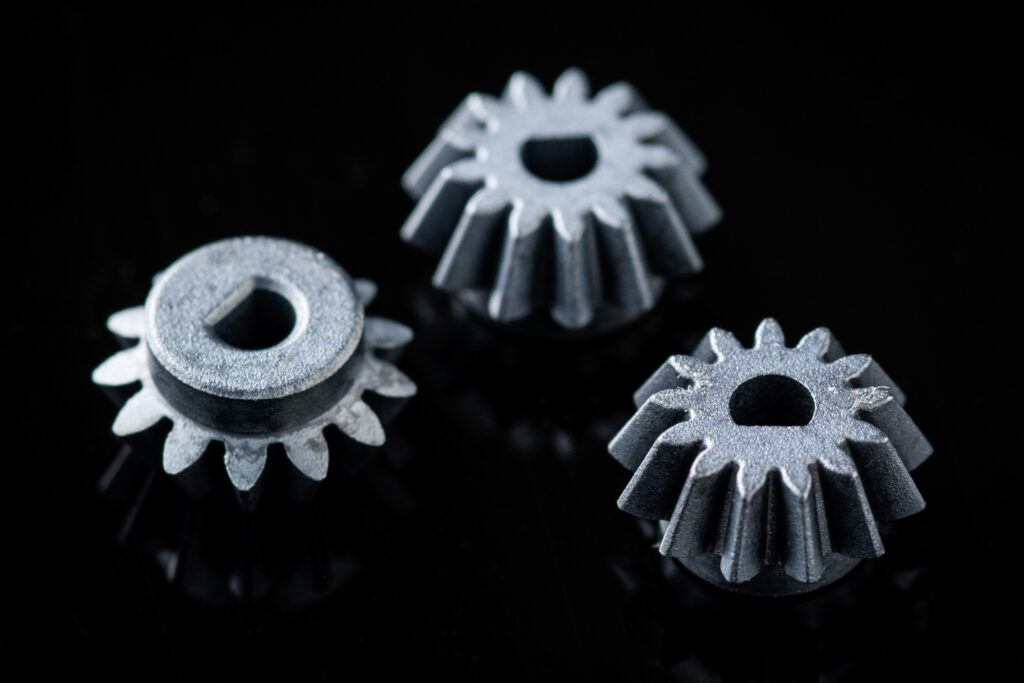
What is a bevel gear?
A bevel gear is a gear shaped like an inclined umbrella, just as the word bevel suggests.
Generally referred to as "bevel gears." Bevel gears are used in combination with other bevel gears. Gears have teeth cut into the side of a cone or a truncated cone, and are used to transmit rotation between two axes that intersect at right angles. When changing the direction of the power to a different axis, or when combining bevel gears, they are installed so that their respective rotation axes intersect. By skillfully using bevel gears to change the direction of power transmission, it becomes possible to transmit power from one power source in any direction. Bevel gears play this role.
Characteristics of bevel gears
Bevel gears are used to transmit motion and power between intersecting shafts. Bevel gears have gear threads that intersect at approximately 90°, allowing them to change the direction of rotational force to a right angle. They are shaped like a cone, like an umbrella, and are used in combination with other bevel gears.
Also, the speed of rotation of a bevel gear is changed by using gears with different numbers of teeth, just like with spur gears.
Manufacturing bevel gears requires a large-scale dedicated gear cutting machine. The most common type is the Gleason type, but others include the Klingelnberg type and the Fiat type.
This is a special example of a method for cutting straight bevel gears, but it is said to be inefficient. A milling cutter designed specifically for cylindrical gears and an indexing machine that can give an inclination equivalent to the cone angle is used to cut each tooth groove.
Bevel gear applications and examples
Bevel gears are used to change the direction of rotation by 90 degrees and transmit power. They are used in coffee mills with large handles, hand mixers and hand drills, as well as radio-controlled cars. Bevel gears are essential for the structure of rear-wheel drive automobiles (trucks, etc.) with the engine and transmission located at the front.
The reason for this is that the power transmitted from the transmission up the propeller shaft needs to be redirected 90 degrees to the rear wheel shaft, and the bevel gear performs this role.
Straight bevel gears are used in differential gears in automobile differential cases, while spiral bevel gears are used in helicopter transmissions, automobile final reduction gears, and screw drive gears in boat outboard motors.
Types of bevel gears
①Straight bevel gear
The advantages of straight bevel gears are that their simple shape allows for high precision and low cost, and because the thrust load is not large, complex bearings are not required.
On the other hand, straight bevel gears make a lot of noise and vibrate when they rotate at high speeds. Straight bevel gears have a small meshing ratio, and the load is placed on a small tooth contact surface, so noise and vibration inevitably increase as the rotation speed increases.
②Helical bevel gears (spiral bevel gears) Helical bevel gears have straight teeth that run at an angle. They have intermediate properties between the "straight bevel gears" introduced earlier and the "spiral bevel gears" that will be described later.
The advantages of helical bevel gears are
•The strength of the teeth is higher than that of straight bevel gears.
•Less vibration and noise than straight bevel gears
This is its characteristic.
The inclined tooth traces provide a high tooth contact ratio, making the teeth stronger than those of straight bevel gears. In addition, the smoothness of meshing is superior to that of straight bevel gears, resulting in less noise and vibration.
3. Spiral bevel gears
→Spiral bevel gears have the advantages of low noise and vibration, high strength, and low wear resistance. They have the disadvantages of being difficult to process and therefore expensive, and of having a large thrust load. Spiral bevel gears are difficult to process because the curved teeth are cut out from a cone-shaped base. The cycle time is longer than other gears, which tends to result in higher costs.
④Miter Gear
There are three types of miter gears: straight miter gears with straight teeth, spiral miter gears with twisted teeth, and zerol miter gears. Standard miter gears may not be compatible with each other even if they have the same module and number of teeth. When miter gears rotate, thrust is applied, which can cause the gears, gear shafts, bearings, etc. to become loose. For this reason, the gears and shafts must be securely fixed together with a key, set screws, knock pins, stepped shafts, etc.
⑤Hypoid gear
Hypoid gears have the advantage of being strong and quiet, and can achieve a large reduction ratio. The high tooth meshing ratio and large tooth contact surface allow for continuous and smooth meshing. In addition, because the axes of the drive gear and driven gear are offset, the meshing surfaces slide in the direction of the tooth trace, making them quieter than spiral bevel gears.
Cons
The disadvantages of hypoid gears are the amount of energy loss and the need to deal with friction. This is due to frictional heat generated by the sliding of the meshing surfaces. If used as is, they will burn out, so the use of gear oil is essential. They are used in automobile drive systems, train drive systems, and reduction gears.
Straight bevel gears
A characteristic of straight bevel gears is that the meshing surfaces and the meshing gears are straight. Because the force acting in the axial direction is small, they are often used in places where thrust loads are undesirable. Another advantage is that they allow for simplified bearings. The disadvantage is that they produce a lot of noise and vibration when rotated at high speeds. Because of these characteristics, straight bevel gears are recommended for use when cost is a priority, high speed rotation is not necessary, or noise is not an issue. They are generally used when operating at relatively low speeds (circumferential speed 2 m/s or less). They are relatively easy to manufacture, and are particularly suitable for machine tools, printing machines, etc., as well as differential devices. They are the most widely used bevel gear for power transmission.
Spiral bevel gear
Also known as a spiral bevel gear. The teeth are spiral and helical, with a twist angle, and the two intersecting gears intertwine with each other to mesh more tightly. The advantages are low noise and vibration even at high speeds, high tooth surface strength, and low load on the tooth surface. In addition, the teeth have curved lines (typically circular arcs) on the pitch cone, allowing for smoother operation compared to straight bevel gears. They are mainly used for high speed operation with a pitch circumference speed of 10 m/s or more.
Zerol bevel gear (spiral bevel gear)
A spiral bevel gear with a helix angle of 0 degrees is also called a zerol bevel gear or a zerol bevel gear. It is a bevel gear that combines the characteristics of a straight bevel gear and a spiral bevel gear, and the force applied to the teeth is the same. A major advantage of this gear is that it can suppress thrust loads compared to a spiral bevel gear. It is used in industrial equipment and automobiles. Its teeth are curved and have a very beautiful appearance, but unlike the tooth profile of a spiral bevel gear, it does not have teeth that are wound in a spiral shape around the outer periphery, and like a straight bevel gear, it is a gear with no twisted teeth.
Hypoid Gear
In a hypoid gear, the axes of the two gears on the input and output sides are staggered and neither parallel nor intersect, and the teeth are spiral.
Although very similar to spiral bevel gears, spiral bevel gears differ in that their axes intersect.
mainly
•Automobile drivetrain
Train drive unit
•Reduction gears (buses, trucks, luxury cars)
It is used in the following ways:
Both are similar in that they utilize a large reduction ratio and are used with large torque.
The advantages of hypoid gears are
・Large reduction ratio
・Low noise and vibration
- Strong enough to withstand large torque
Regarding the reduction ratio, hypoid gears can increase the tooth ratio between the input side (hypoid pinion) and the output side (hypoid gear).
Miter Gear
A gear with the same number of teeth is called a miter gear. The standard shaft angle is 90 degrees, and the pitch surface is 45 degrees. There are also miter gears with 45, 60, and 120 degrees, and the "miter" means a joint or a groove. Miter gears are used in the power transmission, drive, and transport parts of equipment. They can transmit power through orthogonal shafts. They are often used in applications where there is no need to change the speed and only need to change the direction of rotation of a shaft.
It is mainly suitable for use in the semiconductor and food industries, as well as agricultural machinery in addition to general industrial machinery.
For bevel gears, go to Kiyota
We will propose the optimal shape, manufacturing method, production base, and logistics according to your specifications and requests. Since we have sales bases overseas, we can provide you with the best price in one stop. If you have any problems with bevel gears, please feel free to contact us!
FAQ
Q: What are the characteristics of Bevel Gear?
Answer: It enables power to be transmitted in all directions from one power source. Bevel gears fulfill this role.
Question: What are the advantages of ordering bevel gears from Kiyota?
A: We can provide high quality, inexpensive overseas bevel gears. We can offer a variety of manufacturing methods, including plastic, cutting, sintering, and MIM.